1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
|
func schedinit() {
lockInit(&sched.lock, lockRankSched)
lockInit(&sched.sysmonlock, lockRankSysmon)
lockInit(&sched.deferlock, lockRankDefer)
lockInit(&sched.sudoglock, lockRankSudog)
lockInit(&deadlock, lockRankDeadlock)
lockInit(&paniclk, lockRankPanic)
lockInit(&allglock, lockRankAllg)
lockInit(&allpLock, lockRankAllp)
lockInit(&reflectOffs.lock, lockRankReflectOffs)
lockInit(&finlock, lockRankFin)
lockInit(&trace.bufLock, lockRankTraceBuf)
lockInit(&trace.stringsLock, lockRankTraceStrings)
lockInit(&trace.lock, lockRankTrace)
lockInit(&cpuprof.lock, lockRankCpuprof)
lockInit(&trace.stackTab.lock, lockRankTraceStackTab)
lockInit(&memstats.heapStats.noPLock, lockRankLeafRank)
_g_ := getg()
if raceenabled {
_g_.racectx, raceprocctx0 = raceinit()
}
sched.maxmcount = 10000
worldStopped()
moduledataverify()
stackinit()
mallocinit()
fastrandinit()
mcommoninit(_g_.m, -1)
cpuinit()
alginit()
modulesinit()
typelinksinit()
itabsinit()
sigsave(&_g_.m.sigmask)
initSigmask = _g_.m.sigmask
if offset := unsafe.Offsetof(sched.timeToRun); offset%8 != 0 {
println(offset)
throw("sched.timeToRun not aligned to 8 bytes")
}
goargs()
goenvs()
parsedebugvars()
gcinit()
lock(&sched.lock)
sched.lastpoll = uint64(nanotime())
procs := ncpu
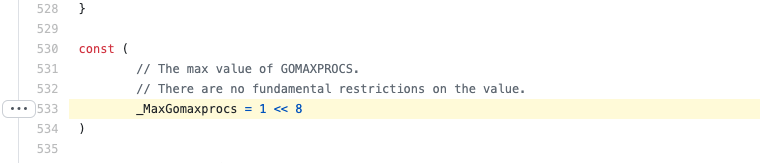
if n, ok := atoi32(gogetenv("GOMAXPROCS")); ok && n > 0 {
procs = n
}
if procresize(procs) != nil {
throw("unknown runnable goroutine during bootstrap")
}
unlock(&sched.lock)
worldStarted()
if debug.cgocheck > 1 {
writeBarrier.cgo = true
writeBarrier.enabled = true
for _, p := range allp {
p.wbBuf.reset()
}
}
if buildVersion == "" {
buildVersion = "unknown"
}
if len(modinfo) == 1 {
modinfo = ""
}
}
|